| H2S System Specifications |
| Liquid flow rates |
0.5 m/s to 2.5 m/s |
| Gas flow rates |
2.0 m/s to 10 m/s |
| Temperature range |
40°C to 90°C |
| Pressure range |
1 bar to 70 bar |
| Liquid mixtures |
Various mixtures of deionized water, synthetic sea water, 2 cP to 10 cP oil, and crude oil |
| Gas Mixtures |
Various mixtures of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and hydrogen sulfide |
| Instrumentation |
Superficial liquid and gas velocities, flow regime determination, corrosion rate, pH, and temperature |
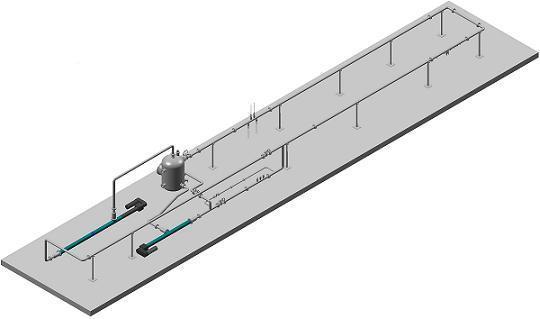
The hydrogen sulfide system is a large scale flow loop currently testing partial pressures of hydrogen sulfide below 150mbar.
The hydrogen sulfide system was commissioned to determine the influence of various concentrations of hydrogen sulfide gas on
corrosion rate in a controlled multiphase environment. This system is comprised of 4" diameter, Sch 80, Hastelloy© C-276 for resistance
to corrosion and stress corrosion cracking, two progressive cavity pumps for conveying liquid and gas, and three separate test sections for
corrosion monitoring.
The hydrogen sulfide system is located in an isolated "environmental chamber" of the Multiphase Technology Center
for better control of temperature and hazardous gases. All operational controls for the hydrogen sulfide test loop are located just outside the
environmental chamber providing a higher level of safety for the operator and more convenience for data collection. Flowing gas mixtures of
methane, nitrogen, and/or carbon dioxide are mixed with flowing liquid mixtures of water and/or oil producing flow regimes of stratified flow,
slug flow, or annular flow in the multiphase environment.
Various types of corrosion-monitoring equipment can be installed in each of two test sections, such as: electrical resistance
probes, linear polarization probes, or coupons for weight loss measurement. With system temperatures capabilities ranging from 40°C to
90°C and pressures from atmospheric to 400 psi, corrosion rate prediction and field simulation tests are easily accomplished in a controlled
environment.




